Libraries (cont.)
Two options to load dynamic libraries:
- Take the DLL file and load it right away
- load - take dll file and put it in RAM memory, so it is accessible by running programs
- loading is time-consuming because we need to copy from hard disk
- only load into RAM when it is needed ("lazy loading")
- allows us to start the program faster, more memory efficient
- BUT, can cause significant delay the first time the DLL is used in the program
Different kinds of builds
Debug build:
- Compiler makes it easy to debug program
- Slower, less efficient
- Compiler adds runtime checks, additional symbols
- Larger executable
- Makes it easier to find problems
- Type of build that is usually done when writing code
Release build:
- As fast as possible
- As small as possible
- Compiler optimizations enabled typically
- Ballpark estimate for speedup compared to debug build, with compiler optimizations - around 10x faster
CPU design
Relevant reminder items for this section:
- Logic gates (input and output)
- Hardware that implements boolean functions
- Flip-flops and latches
- not discussed in this couse, but are used to store 0 or 1 - trap the bit value
- used to create memory
We use flip-flops to construct registers because they are fast:
- for example, 32-bit registers have 32 flip-flops
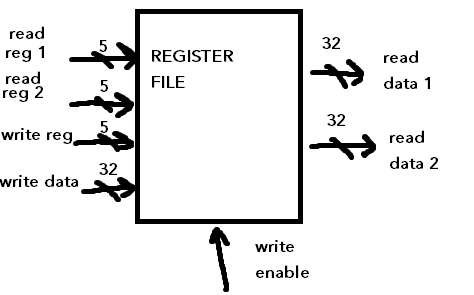
Registers and Register File
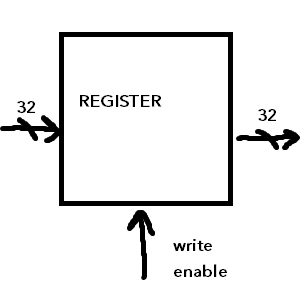
- 32 wires go into the register
- inputs to flip-flops to deliver new values
- "write enable" - register is only updated if this input is 1, otherwise it ignores new values
- also, 32 outputs, that always show the outputs of the register (values currently stored)